Page 38 - MMP-N-NJ CCN 21st Century School Nurse Leadership Book
P. 38
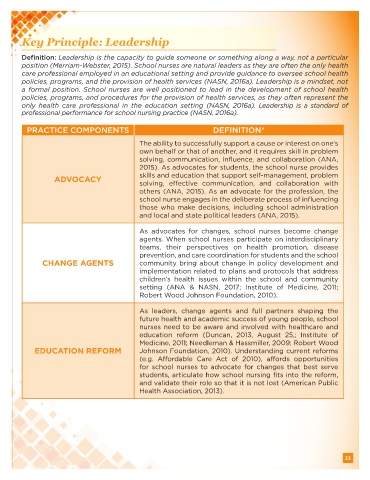
Key Principle: Leadership
Definition: Leadership is the capacity to guide someone or something along a way, not a particular
position (Merriam-Webster, 2015). School nurses are natural leaders as they are often the only health
care professional employed in an educational setting and provide guidance to oversee school health
policies, programs, and the provision of health services (NASN, 2016a). Leadership is a mindset, not
a formal position. School nurses are well positioned to lead in the development of school health
policies, programs, and procedures for the provision of health services, as they often represent the
only health care professional in the education setting (NASN, 2016a). Leadership is a standard of
professional performance for school nursing practice (NASN, 2016a).
PRACTICE COMPONENTS DEFINITION*
The ability to successfully support a cause or interest on one’s
own behalf or that of another, and it requires skill in problem
solving, communication, influence, and collaboration (ANA,
2015). As advocates for students, the school nurse provides
ADVOCACY skills and education that support self-management, problem
solving, effective communication, and collaboration with
others (ANA, 2015). As an advocate for the profession, the
school nurse engages in the deliberate process of influencing
those who make decisions, including school administration
and local and state political leaders (ANA, 2015).
As advocates for changes, school nurses become change
agents. When school nurses participate on interdisciplinary
teams, their perspectives on health promotion, disease
prevention, and care coordination for students and the school
CHANGE AGENTS community bring about change in policy development and
implementation related to plans and protocols that address
children’s health issues within the school and community
setting (ANA & NASN, 2017; Institute of Medicine, 2011;
Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, 2010).
As leaders, change agents and full partners shaping the
future health and academic success of young people, school
nurses need to be aware and involved with healthcare and
education reform (Duncan, 2013, August 25,; Institute of
Medicine, 2011; Needleman & Hassmiller, 2009; Robert Wood
EDUCATION REFORM Johnson Foundation, 2010). Understanding current reforms
(e.g. Affordable Care Act of 2010), affords opportunities
for school nurses to advocate for changes that best serve
students, articulate how school nursing fits into the reform,
and validate their role so that it is not lost (American Public
Health Association, 2013).
33